For the unaware, IPC (instructions per cycle) provides a good indicator of how fast a processor is and having both a high IPC with a high operating frequency is the best combination for maximum performance. Such is the case for Intel's 8th-Gen Coffee Lake CPUs, and although AMD is clearly trailing when it comes to frequencies, the company appears to have really closed in on Intel's IPC performance. That's likely the reason why so many of you have been asking for this kind of test.
To see how much headway AMD has made here, we're going to limit as many variables as we can, while also keeping things as realistic as possible. The first and most obvious step is to remove core frequency from the equation and to do this we've locked all of the CPU cores at 4GHz. Any type of boost technology has been disabled and the cores cannot go past 4GHz.
The second-gen Ryzen CPUs were tested on the Asrock X470 Taichi Ultimate and the Coffee Lake CPUs were on the Asrock Z370 Taichi. Both configurations used the same G.Skill FlareX DDR4-3200 memory with the 'Xtreme' memory profile and the same MSI GTX 1080 Ti Gaming X Trio for all the testing.
We can say upfront that this article is in no way buying advice, but we're testing purely for the science of it.

The Coffee Lake CPUs have a clear clock speed advantage. For real-world performance, please refer to our recent Ryzen 5 2600, 2600X and 2700X reviews.
For this test we've included results for the Intel Core i7-8700K, 8600K, Ryzen 7 2700X, 2600X and Ryzen 7 1800X along with the 1600X. Now, the 1600X, 2600X and 8700K all have the same CPU resources: 6 cores with 12 threads.
The 1800X and 2700X have an advantage being that they are 8-core/16-thread CPUs while the 8600K is at a disadvantage as it's a 6-core/6-thread CPU, so please keep all that in mind as we proceed. Let's get to the results.
Benchmarks
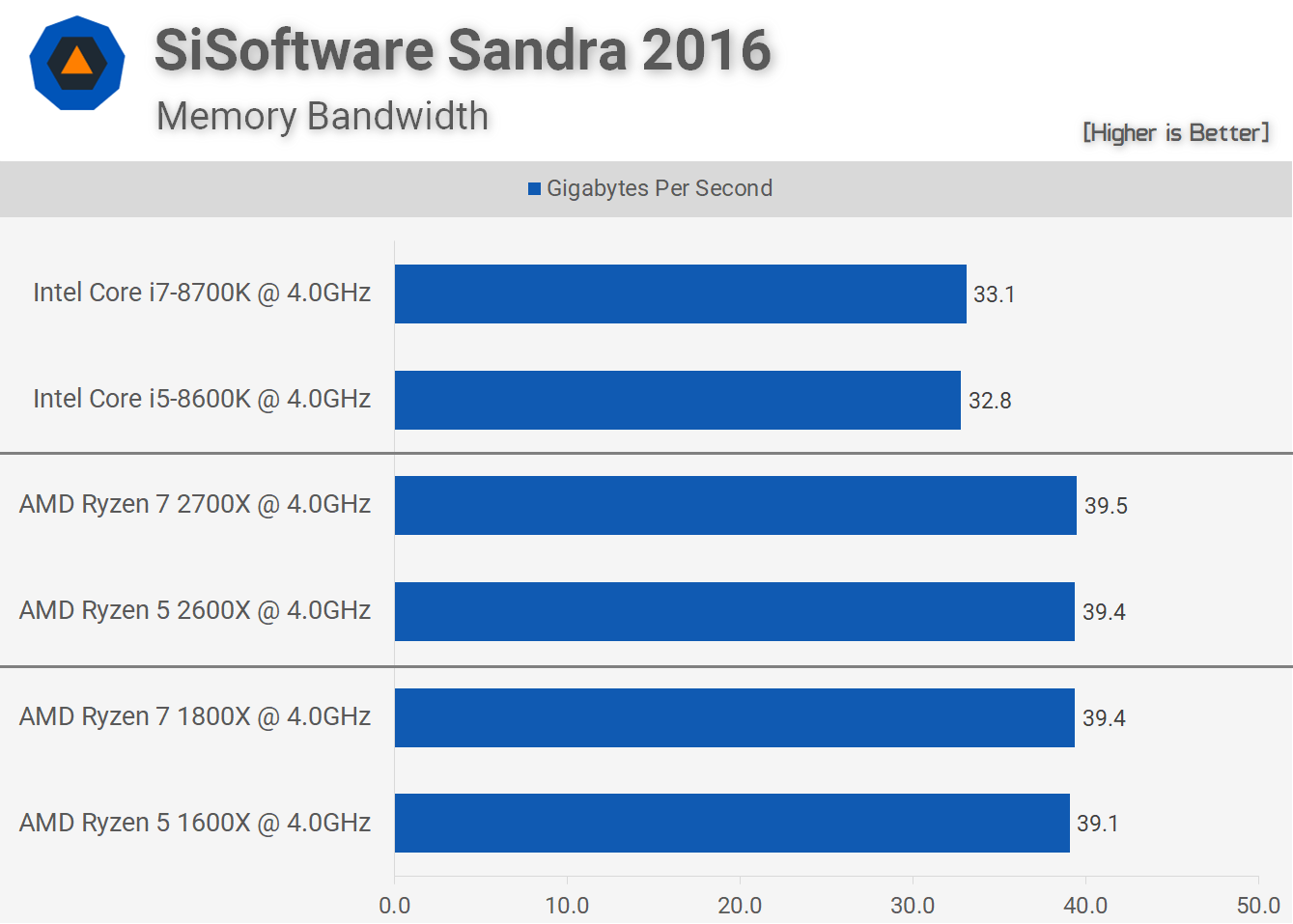
Starting with the sustained memory bandwidth test we see that the first and second-gen Ryzen CPUs are similar with a bandwidth of about 39GB/s. Meanwhile, using the exact same memory, the Coffee Lake CPUs are limited to around 33GB/s and this is a 15% reduction in bandwidth when compared to the Ryzen CPUs.
Moving to Cinebench R15 we see that the 2600X scores 4% higher than the 1600X for the multi-threaded test and 3% higher for the single thread score. Then as we look at the 8700K we see that it's 4% faster than the 2600X for the single thread score but 4% slower for the multi-threaded score.

As you might have expected, clock-for-clock the 8-core/16-thread Ryzen CPUs easily beat the multi-threaded score of the 8700K. I included them simply because I had the results. Depending on demand, I could update this test with the Core i7-7820X for example.
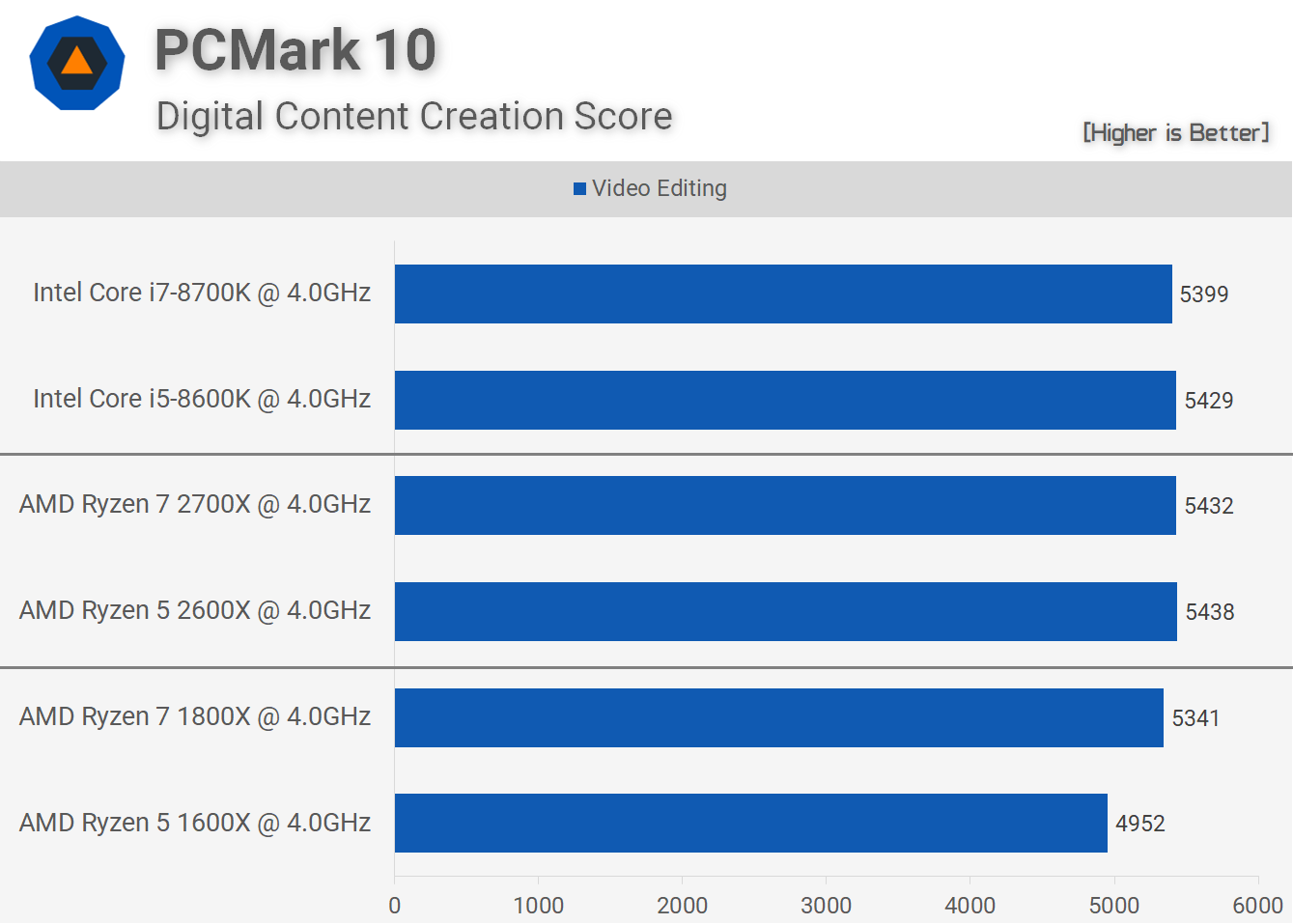
Next up we have the PCMark 10 video editing scores and this is a more lightly threaded test though we did previously see a noteworthy difference between the 1600X and 1800X. As a result we see a solid 10% jump from the 1600X to the 2600X and this places AMD on par with Intel in terms of IPC performance for this test.
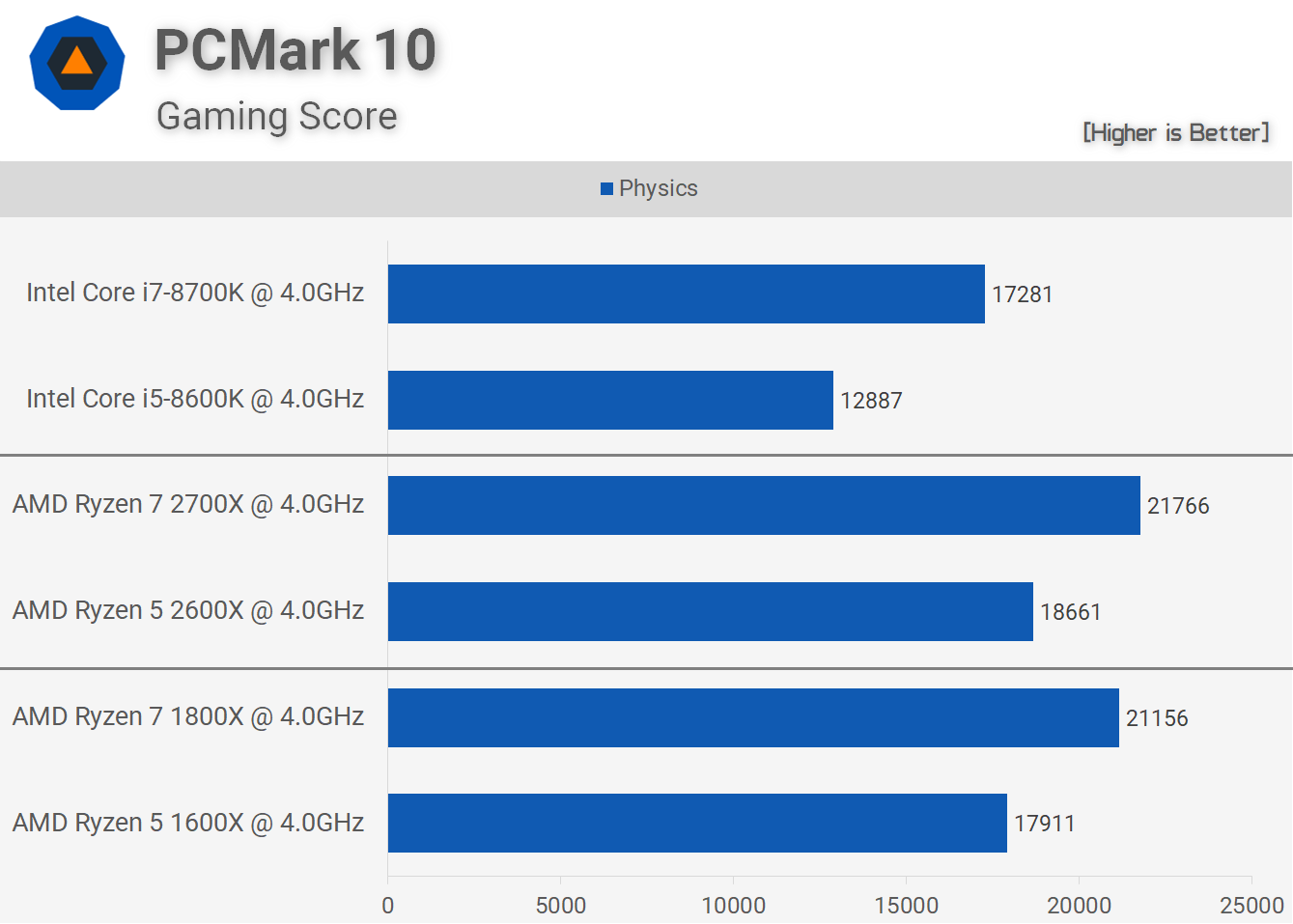
Like what we saw with Cinebench R15, when maxed out SMT appears more efficient than Intel's HT technology. Here the 1600X was faster than the 8700K by a 3.5% margin while the 2600X was 8% faster and that's a noteworthy margin right there.
